It's time once again to revisit the critical temperatures that can cause frost damage to fruit trees, specifically apple trees. We are currently at full bloom here in northern Illinois with a frost advisory forecast for tonight. This spring has marked another unprecedented weather pattern that raised
our temperatures in late March and early April and dropped our temperatures in late April to
below normal. The early warm temperatures accelerated tight cluster on into bloom and now at full bloom the lower temperatures are effecting pollination and the threat of frost during bloom. It seems that each spring since 2012, we have been on the
verge of critical temperatures for frost damage with our fruit trees.
 |
| The dark brown center of this apple flower indicates it was killed by a freeze. (Photo credit: Mark Longstroth, MSU Extension) |
Given
the weather patterns we have experienced so far this spring a spring frost could
be possible. Once the fruit has set, then the critical temperatures that can damage the fruit become lower. We will need to constantly
assess the stage of development our trees are at over the next weeks and their
susceptibility to possible freeze injury.
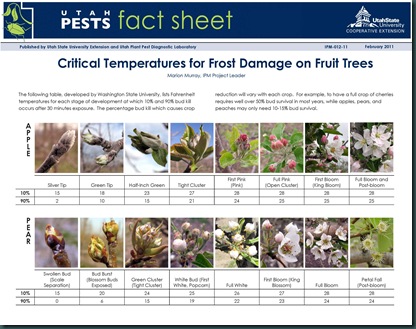
If we continue in this spell of colder weather, apple trees will continue to develop more slowly, but once they begin showing tight cluster, pink and bloom, the critical temperature rises from the low 20’s to the high 20s, to levels just below freezing at bloom time, which is where we are now.
If we continue in this spell of colder weather, apple trees will continue to develop more slowly, but once they begin showing tight cluster, pink and bloom, the critical temperature rises from the low 20’s to the high 20s, to levels just below freezing at bloom time, which is where we are now.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments are welcome! All comments are moderated, so you will see your comment posted here as soon as we have reviewed it! Questions are best asked via email for a quicker response. Address your questions to service@royaloakfarmorchard.com.
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.